
Cross flow fans are very good at saving energy for new ventilation needs. Their shape lets air move smoothly and evenly. They use less power, so they help businesses save money. Energy-saving ventilation systems have many good points:
Utility bills go down because less energy is used for heating and cooling
HVAC equipment lasts longer because it works less hard
Building value goes up and it helps with being more eco-friendly
LONGWELL’s cross flow fan products are known for being dependable and quiet in many types of businesses and factories.
Key Takeaways
Cross flow fans have a special shape that moves air gently and evenly. This helps save energy and lowers your power bills. – Look at the fan efficiency ratio and specific fan power. These help you choose fans that use less electricity and save money over time. – The right fan design, size, and where you put it help keep energy use low. They also keep airflow steady in many situations. – Cleaning and taking care of fans often helps them run quietly and well. This also makes them last longer. – Cross flow fans are quieter and use less energy than many other fans. This makes them great for offices, homes, and small rooms.
Cross Flow Fan Basics

What Is a Cross Flow Fan
A cross flow fan has a long, round part called an impeller. The impeller has many blades that curve forward. It sits inside a case with panels on both ends. This setup makes air move sideways through the fan. Other fans move air in different ways. Axial fans push air along the shaft. Centrifugal fans move air outward. Cross flow fans send air across the whole length. This gives a wide and even stream of air. Other fans often make narrow or uneven airflow.
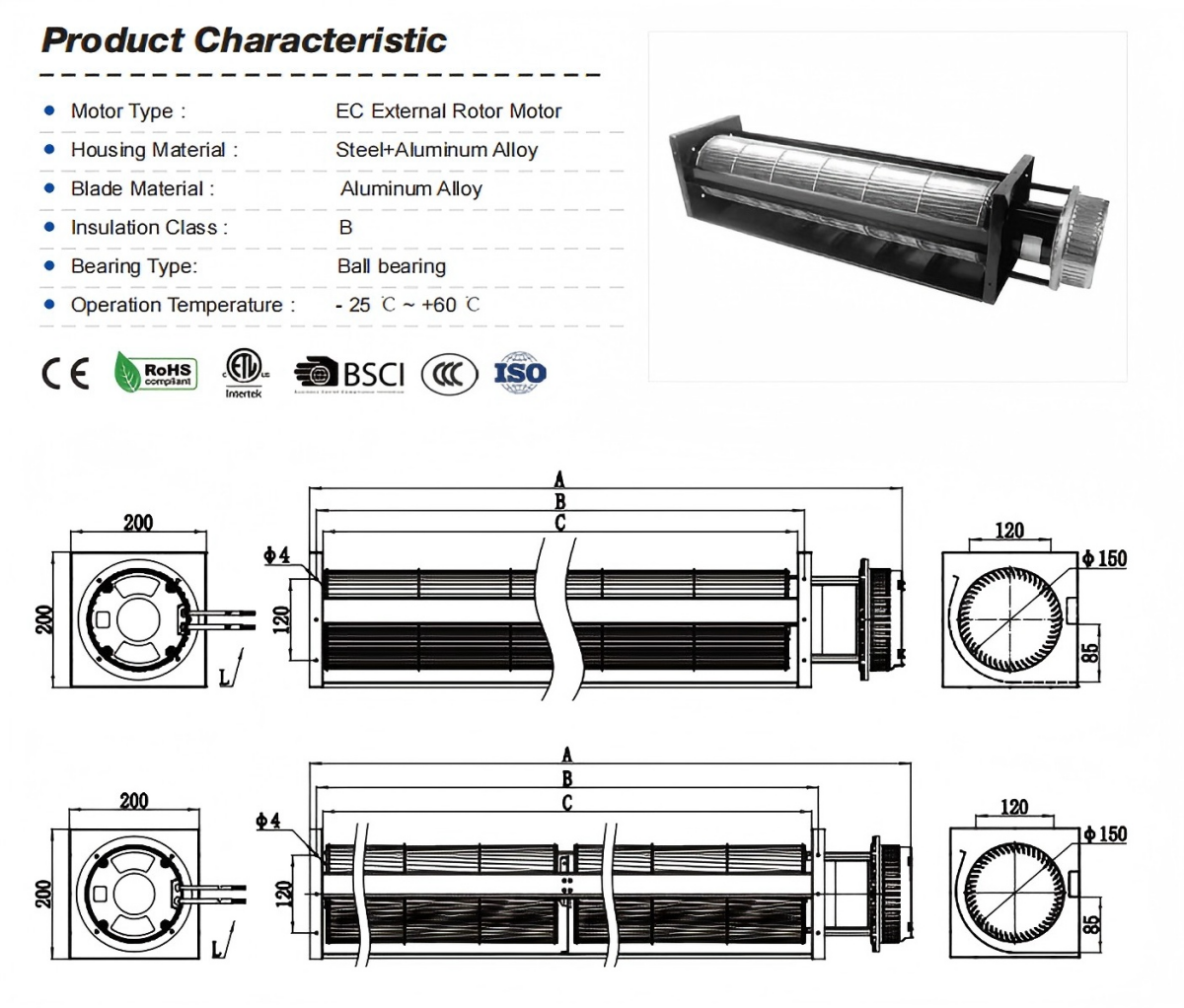
The main parts are the impeller, air duct, and motor. The impeller is made from aluminum alloy or strong plastic. The air duct is shaped to help air move smoothly. This shape also helps save energy. The motor can be AC or DC. It connects to the impeller and makes it spin. These parts help the fan give steady airflow. The fan is also quiet and uses little energy.
Note: Cross flow fans are used in HVAC systems, air curtains, electronic cooling, home appliances, and industrial machines. They are chosen because they give wide and even airflow.
How Cross Flow Fans Work
Cross flow fans pull air in along the impeller’s length. The air goes through the blades and comes out the other side. Inside, a special vortex forms. This vortex acts like a seal. It helps control the air and saves energy. The air moves sideways to the shaft and along the impeller. This makes a flat, two-dimensional flow.

Engineers can change the fan’s design to make it better. They might change the vortex wall’s angle or the case’s shape. These changes help air move better and waste less energy. Studies show these changes can make the fan work up to 12% better. The way cross flow fans move air helps them use less energy. They still give strong and even airflow.
Component | Function |
|---|---|
Impeller | Moves air through the fan |
Air Duct | Guides airflow and reduces energy loss |
Motor | Powers the impeller (AC or DC options) |
Cross flow fans are known for being efficient, quiet, and giving even airflow. This makes them a great choice for new ventilation needs.
Energy Efficiency Metrics

Fan Efficiency Ratio
The fan efficiency ratio shows how well a fan uses power. It tells us how much airflow comes from the electricity used. This helps people compare different fans. If the ratio is higher, the fan saves more energy. Cross flow fans often do well because of their special design. The long impeller and air duct help stop energy loss. These parts let the fan give wide airflow but use less power.
Companies like LONGWELL make cross flow fans to get the best ratio. They use strong motors and shape the impellers carefully. These changes help the fans work better and save energy. When buildings use fans with a high ratio, they use less energy. This also means lower costs for running the building.
Tip: Always look at the fan efficiency ratio before picking a fan. This number shows how much energy the fan will use over time.
Specific Fan Power
Specific fan power, or SFP, is another way to check energy use. SFP tells us how much power a fan needs to move air. If the SFP is lower, the fan uses less energy for the same job. This is important when you want to compare fans.
The table below shows SFP values for HVAC systems, including cross flow fans:
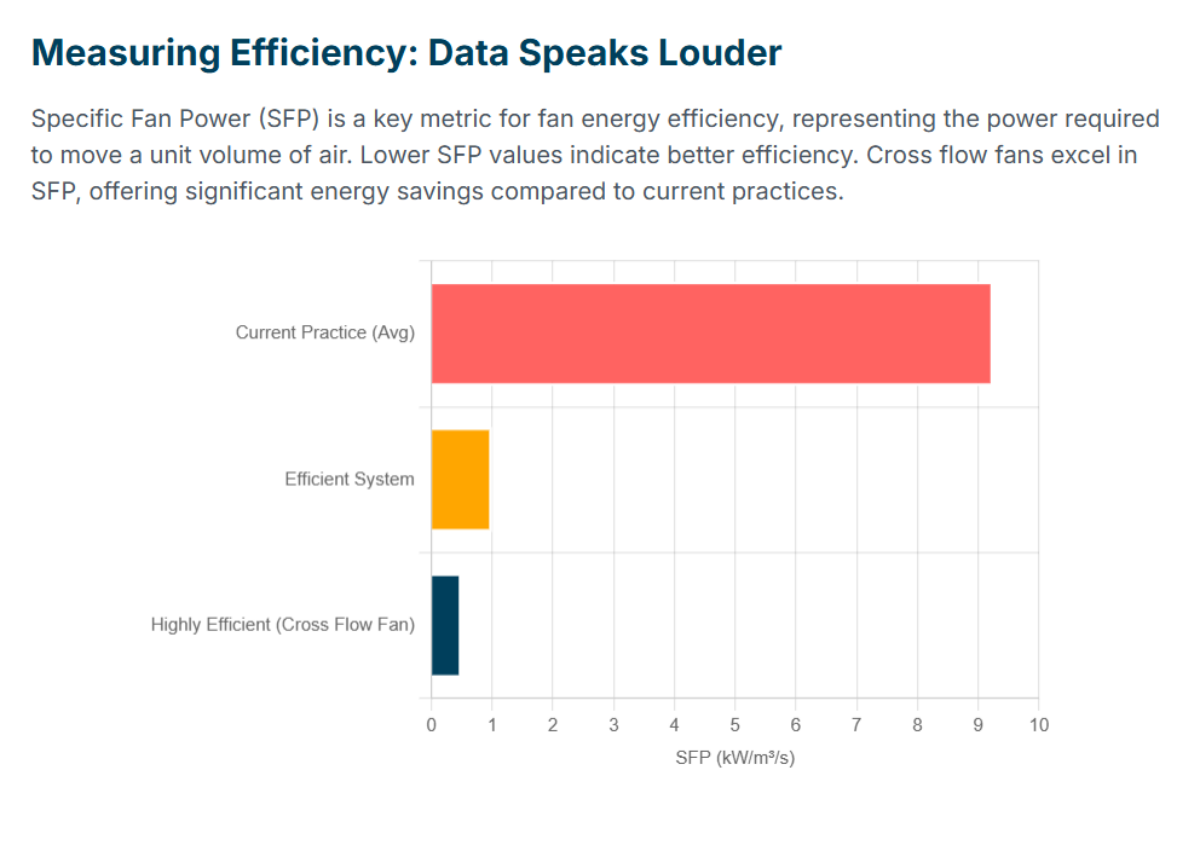
System Type | Specific Fan Power (kW/m³/s) |
|---|---|
Very efficient | ~0.5 |
Efficient system | ~1 |
Current practice | 5.5 – 13 |
Studies of almost 1,000 fans show good design helps SFP. Most fans have SFP between 0.5 and 1 kW/m³/s. The average SFP, based on motor power, is about 1.5 kW/m³/s. This means cross flow fans in buildings often have SFP from 0.5 to 1.5 kW/m³/s. These numbers show that new cross flow fans, like LONGWELL’s, can help save energy in ventilation.
Note: Picking fans with low SFP can save a lot of money on energy bills. It also helps buildings be more eco-friendly.
Factors Affecting Cross Flow Fans
Design and Sizing
How cross flow fans are made and sized is very important. These things decide how well the fan works and saves energy. Engineers look at many features to help air move better and waste less energy.

Blade Shape: Blades that are curved and twisted help air move easily. This shape stops rough air and makes less resistance. The motor does not need to work as hard.
Blade Angle: Each blade must be set at the right angle. If the angle is too small, the fan moves less air and pressure. If the angle is too big, it makes more resistance, noise, and uses more energy.
Blade Number: More blades can make airflow smoother. But too many blades can cause more resistance and noise. If there are not enough blades, the fan cannot move much air.
Blade Material: Blades made from plastic or aluminum are light. These materials help the motor use less power. Heavy blades like steel make the motor work harder and use more energy.
Application-Specific Design: Fans made for a special job can be quieter. They can also cost less to fix and help air stay clean.
Picking the right size fan is important for each space. If the fan is too big, it wastes energy. If it is too small, it cannot move enough air. LONGWELL has many sizes and custom choices for different needs.
Operating Conditions
How the fan works depends on the air and the place. Air temperature and humidity can change how hard the fan must work. When the air is hot or wet, it is harder for the fan to move air. This can make the fan less efficient.
Hotter air and more wet surfaces can help cooling systems work better.
More humidity can make direct evaporative cooling less efficient. But crossflow designs can help with this problem.
The materials and how air moves in the system change how heat and water move. This affects how well the fan works.
Studies show that higher air temperature and more air moving can make the system work better.
Tests show that cooling can get better and air can get cooler by up to 7 °C.
If the temperature difference is more than 5 °C, sensible heat exchange matters more. But changing the air ratio does not change temperature and humidity much.
New designs and materials help fans work well in both dry and wet places.

Tip: Put fans in the right spot, leave space around them, and check temperature and humidity to keep them working their best.
Maintenance
Taking care of cross flow fans helps them last longer and work well. If you do not take care of them, they use more energy and move less air.
Clean the blades and case to stop dust from building up. Dust can block air and make the motor use more power.
Check and fix blade balance to stop shaking. Shaking can break parts and make the fan less efficient.
Oil the bearings to lower friction. This helps the fan run smoothly and saves energy.
Stop rust to keep parts strong and working well.
Make a schedule for checks, cleaning, oiling, and big checkups. This keeps the fan in good shape.
Some problems are clogged filters, hot motors, and water flow issues. Dirt in the air can block strainers and heat exchangers. This makes cooling worse. If there is no filter, dirt can get in and lower airflow. Clean fill packs, strainers, and filters often to keep the fan efficient. If the motor gets too hot, it could be from low voltage or an unbalanced fan.
Note: Many cross flow fans, like those in cooling towers, are easy to reach for maintenance. This makes it simple to take care of them without stopping the system. It helps save energy for a long time.
Cross Flow Fans vs Other Fans

Energy Efficiency Comparison
When you look at cross flow fans and other fans, you see some big differences. Cross flow fans usually use less power than centrifugal fans of the same size. Their simple shape and low-pressure work help save energy. These fans can move a lot of air without much trouble. Centrifugal fans can make more pressure, but they need more energy to do it.
Cross flow fans work well at low pressures.
They give even airflow over wide areas.
Their small, round shape fits in tight spaces.
Centrifugal fans are good for high-pressure jobs but use more power.

Cross flow fans save more energy in places that need steady, low-pressure airflow. They are great for air conditioners, air curtains, and cooling electronics.
Airflow and Noise
Airflow and noise are important when picking a fan. Cross flow fans are known for being quiet. Their long impeller and even air spread help keep noise down. This makes them good for offices, homes, and other quiet places.
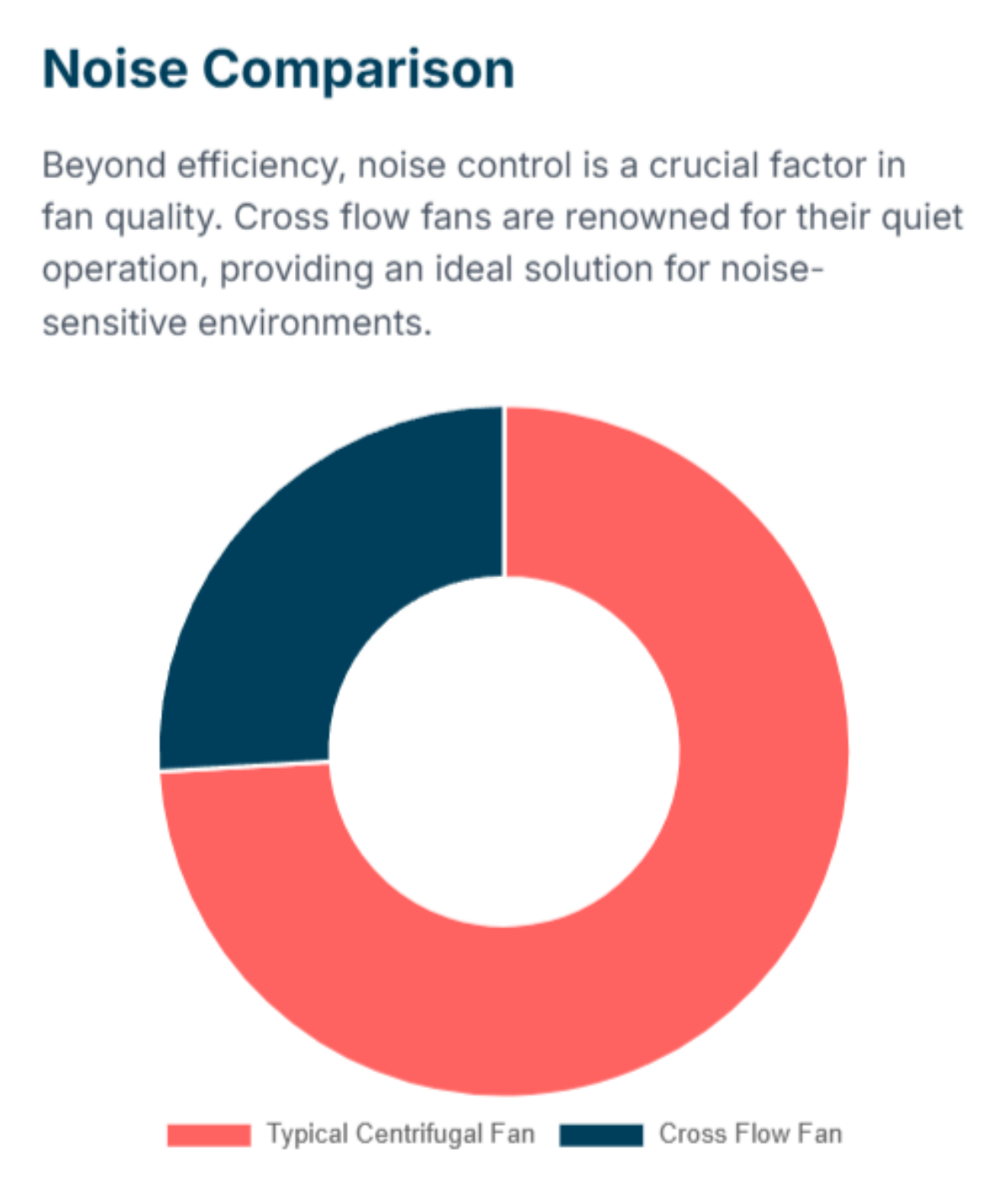
Fan Type | Noise Level Characteristics |
|---|---|
Cross Flow Fans | Usually quiet, even airflow, small shape |
Centrifugal Fans | Often louder, faster air, bigger impellers |
How a fan is made changes how it moves air and how loud it is. Changing the rotor skew angle in cross flow fans can make them quieter but still move air well. A medium skew angle keeps things quiet and keeps up the pressure. A bigger skew angle can make the fan even quieter, but it might make higher-pitched sounds. This helps engineers pick the best airflow and noise level for each job.
Tip: If you need a fan that is quiet and gives steady air, cross flow fans are a great choice.
Applications of HVAC Cross Flow Fans
Industrial and Commercial Uses
HVAC cross flow fans are important in many buildings and machines. They are small and quiet, so they fit where space and noise matter. These fans give smooth airflow. This helps keep the temperature steady and keeps equipment safe.
Some common uses for HVAC cross flow fans are:
Air curtains in stores and offices. These keep inside and outside air apart. This helps save money on heating and cooling.
Cooling electronics. The fans blow steady, quiet air. This stops parts from getting too hot.
Elevators and transformer boxes. These places are small and need even airflow.
HVAC systems in offices, hospitals, and schools. These places need quiet and steady air movement.
Home appliances like ovens, microwaves, and air conditioners. These need to be quiet and small.
Axial fans work best in big open spaces. HVAC cross flow fans are better in small places that need even airflow.
LONGWELL Product Highlights
LONGWELL makes many HVAC cross flow fans. Their fans are made to be efficient and reliable. They have AC, DC, and EC models. Each type has its own good points.
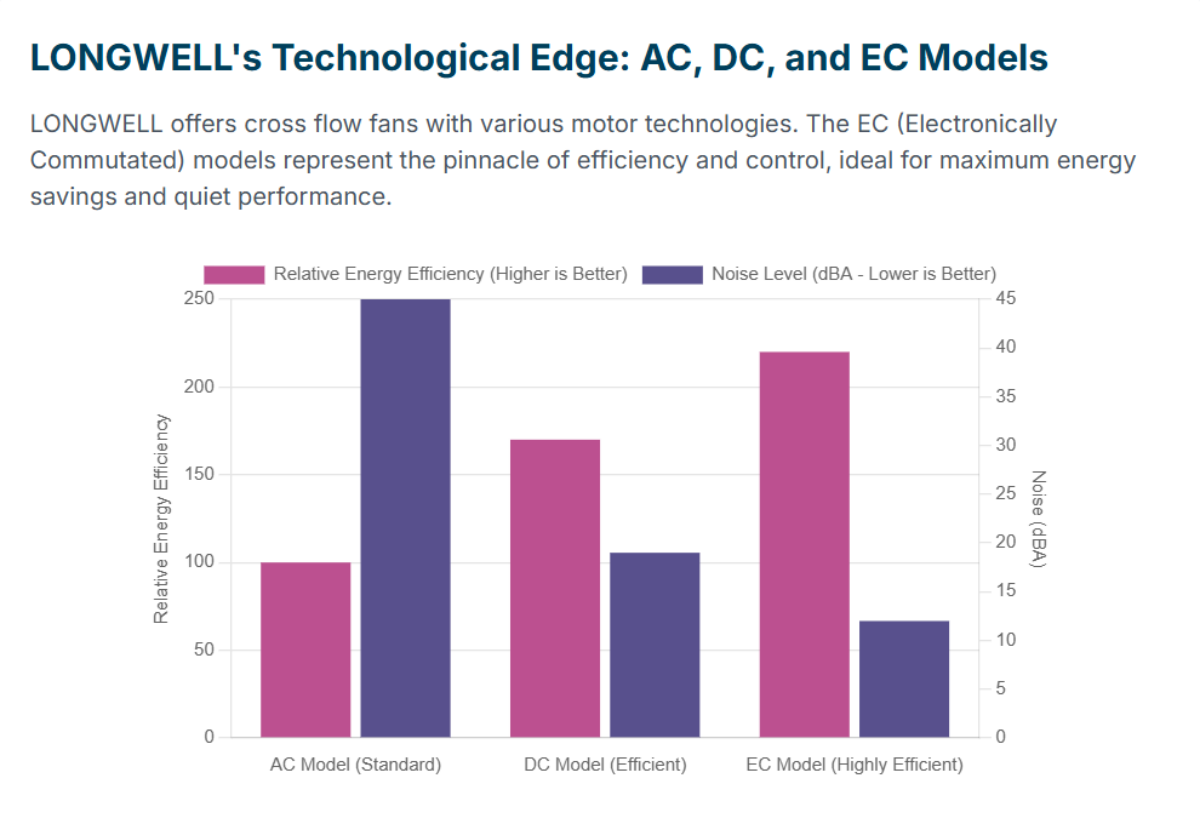
Fan Type | Motor Technology | Energy Efficiency | Speed Control | Noise Level | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
AC | Shaded pole | Standard | Fixed | Moderate | Strong, simple build |
DC | Brushless DC | Variable | Low (19 dBA) | Works in very hot or cold places | |
EC | EC brushless DC | Highest | Precise | Very low (12 dBA) | Even airflow, lasts a long time |
LONGWELL has special models for different needs. Their fans come in many sizes. The impeller can be from 30mm to 150mm wide and up to 1300mm long. Some fans have speed control, temperature sensors, and ball bearings that do not need oil. LONGWELL also makes custom fans for special jobs. Their fans work with many voltages and meet tough world rules. This means they save energy and last a long time in any job.
Note: LONGWELL’s HVAC cross flow fans are quiet, strong, and save energy. This makes them great for new ventilation systems.
Choosing an Efficient Cross Flow Fan
Selection Tips
Picking the best cross flow fan means thinking about many things. Here are some important points to help you choose:
Airflow Rate and Flow Resistance: Make sure the fan gives enough airflow. Check that filters or ducts do not block air too much. Too much resistance can make the fan less efficient.
Operating Parameters (Back Pressure): Pick a fan that can handle the right back pressure. This keeps the airflow steady and stops stress on the fan.
Temperature Considerations: Choose fans that do not get too hot inside. Good heat control is important in hot places or with brushless motors.
Shock and Impact Resistance: Get fans that can take bumps and hard use. This helps the fan last longer.
Bearing Quality: Good bearings help the fan run smoothly. They also make the fan last longer by lowering friction.
Noise and Vibration Resistance: Find fans that are quiet and do not shake much. This makes the space more comfortable and saves energy.
Design and Dimensions: The fan’s size and shape should fit the job. Small and flexible fans are good for tight spots.
LONGWELL has many cross flow fans with different features. Their team can help you pick the best fan for your needs. This helps save energy and keeps the fan working well.
Tip: Talk to LONGWELL’s experts about options like speed control, better bearings, and special materials for tough jobs.
Installation and Maintenance
Putting in the fan the right way and keeping it clean helps it work well for a long time. LONGWELL’s EC models need less care because they have brushless motors. But all fans need regular checks and cleaning. Checking and cleaning stops dust from blocking air and keeps the fan efficient. These easy steps help the fan last longer and work better.
Check the fan often to find problems early.
Clean the blades and case to keep air moving well.
Change old parts when needed to stop breakdowns.

Note: LONGWELL’s team can help with installing and caring for your fan. This helps you get the best use from your cross flow fans.
Cross flow fans help save energy in new ventilation systems. Two important things to check are Fan Efficiency Ratio and Specific Fan Power. These show how well the fans use electricity. Picking the right size, keeping noise low, and making cleaning easy are also important. Many businesses pick cross flow fans because they move air well and do not use much energy. LONGWELL has good choices for people who want fans that save energy and work well. If you want more help or special advice, you can talk to LONGWELL’s support team.
FAQ
What makes cross flow fans energy efficient?
Cross flow fans have a special impeller and air duct. This design helps air move smoothly. It also stops energy from being wasted. LONGWELL’s fans use strong motors and good materials. These things help the fans use less power.
Where can LONGWELL cross flow fans be used?
LONGWELL cross flow fans work in many places. They are used in elevators and HVAC systems. They help cool electronics and transformer boxes. You can also find them in home appliances and air curtains for businesses.
How do LONGWELL’s EC cross flow fans save more energy?
LONGWELL’s EC cross flow fans have special motors. These motors can change speed very exactly. This helps the fans use less power. The airflow stays steady while saving energy.
Are cross flow fans noisy during operation?
Most cross flow fans are quiet when running. LONGWELL’s fans have special blade shapes and good bearings. This keeps noise low, even in quiet places.
How often should cross flow fans be maintained?
Fans need to be cleaned and checked often. LONGWELL says to look at blades, bearings, and filters every few months. Taking care of fans helps them last longer and use less energy.